DMA Partitioned
DMA Classification
DMA Techniques
DMA Partitioned
The DMA Partitioned Management is to build isolated regions in the water supply system by closing the valve or installing a flow instrument. These regions are either virtual or real. By counting the water volume flowing into or out of a region, and analyzing the data, workers could decide when and where to check the pipeline and take precautions for leakage actively.
As a part of the Water Supply Pipeline Network Management System, the DMA Partitioned Management enables the water distribution system to run systematically. Besides, it also strengthens human resources management, which effectively reduces the distribution losses in water supply. In a word, the DMA Partitioned Management helps alleviate distribution losses and maximize water suppliers’ profit.
1. Objectives for DMA Partitioned Management
To optimize enterprise management, clarify rights and duties of each department in water supply companies, and focus ourselves on the most profitable business are the main objectives for the DMA Partitioned Management. Through the DMA Partitioned Management, we keep a close eye on the water supply system, analyzes data collected from the pipeline network, and diagnose pipeline leakage, which provides scientific support for network management.
Briefly speaking, the implementation of DMA Partitioned Management contributes to narrowing the distribution loss rate, distributing resources including manpower and materials rationally, and forming a more scientific and rational operation pattern for water suppliers. Therefore, a long-term control on leakage and loss is the main target for DMA Partitioned Management. Details are as follows:
(1)It provides references for regional reconstruction of water supply pipeline network, maintenance of measuring instruments, and water supply planning.
(2)It takes positive action to inspect leakages of the pipeline network and locates the leakage position precisely so as to fix the problem swiftly and reduce water loss.
(3)It helps water supply administrative departments detect accidents like tube burst and leakage in time.
(4)Targeted management and control of pressure are feasible by adjusting water pressure in DMA regions to the optimal degree, which enables the pipeline network to operate under an optimal pressure. It helps lower the bursting rate and the physical loss of water and hence improves water supply service.
(5)Targeted updating and maintenance of investment makes it more systematic.
2. Input of the DMA Partitioned Management
The establishment of DMA Measuring Management Zone demands for constant personnel management. To make sure the data of flows in pipelines is true and accurate, we should add the amount of flow instruments or even change them. Moreover, we should add the number of or transform valves to assure the pipeline is well-sealed. Or the data collected might be misleading or useless. Therefore, the DMA Partitioned Management needs capital investment.
1. The DMA Partitioned Management is to divide the pipeline network into several individual regions by cutting off the pipe or closing valves on pipelines and then installing flow instruments on the inlet and outlet side of a pipe in each region through which water flows into and out of a region could be counted.
Water suppliers used to play a passive role in leakage inspection. They try to pinpoint problems and fix them only after losses are caused, which extends the duration of leakage and increases their gross loss. Even the leakage inspection company cannot lower the risk of leakage and damage substantially for leakages could not be eradicated. Only through accurate measurement at night and real-time monitoring on noise, the leakage position could be pinpointed and the problem of leakage and damage would be controlled under a man-made rational pressure. Subsequently, the distribution loss could be reduced.
2. Learning from successful experiences abroad, we classify the DMA into three types according to the amount of users:
a) Large-Scale (Number of users: 3000~5000)
b) Middle-Scale (Number of users: 1000~3000)
c) Small-Scale (Number of users: ≤1000)
The DMA could also be classified into three types according to pipelines:
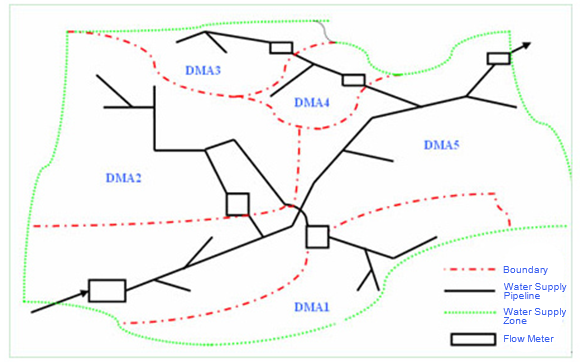
a) Delivery Pipe (See DMA1 in Figure 1)
b) Distribution Pipe (See DMA2 and DMA5 in Figure 1)
c) Tiered Type (See DMA3 and DMA4 in Figure 1)(Water in DMA flows down from the upper layer to the lower, which appears to be tiered.)
1.Step-by-Step Closed Water Test
Step-by-Step Closed Water Test is one of the most effective methods to narrow the scope of leakage in pipeline network. It is mainly adopted in DMA regions or temperately-isolated areas which are capable of reading data on flows. While leakage happens in these areas, the severely affiliated areas could be figured out simply through opening and closing the valve. This technique is reliable and accurate in positioning, which quantizes leakage and ullage in specified areas.
2. Acoustic Leakage-Detection Technique
The Acoustic Leakage-Detection Technique follows the principle of “field-line-point” and takes turns to use patrol instrument, correlometer and leakage listening detector to narrow the sphere of leakage and improve efficiency. Details of it are as follows:
(1)Patrol Instrument is a leakage-detection instrument capable of pre-positioning. It could monitor leakage in fixed monitoring sphere. However, the exact position of leakage could not be pinpointed.
(2)Correlometer is used mainly for general examination and location of the leakage position, which could pinpoint the leakage position (generally within a range of 2 meters).
(3)Leakage Listening Detector is the most widely used leakage-detection instrument which is generally used for leakage positioning and confirming.
3.Gas tracer detection technology
First infuse some gas (helium) into the pipeline. Next the gas leaks out with water while holes appear on pipelines. Then we could use detection instruments to pinpoint leakage positions. This technique is mature and it positions precisely. It could detect as many leakage points as possible at once.
4. Nighttime Flow Analysis
The nighttime flow suffers little influences from seasonal change. Therefore, leakages could be easily detected through analysis on the minimum flow such as a surge of the water flow at night, which helps the pipelines maintained in time.
5.Pressure Management
Pressure management is to restrict the pressure of the pipeline system to its optimal level. It from the side assures that there is enough water for legal customers to use. From the other side, it lowers the steep pressure inside of the pipeline and hence reduces the bursting and leakage rate. In this way, the leakage rate will be kept on an optimal level.
6.DMA Partitioned Management Platform
Through multiple data cross-analysis, the distribution loss management module establishes a hydraulic model according to collective data of water flow, nighttime flow, pressure management and leakage noise detection.
The platform has functions including data analysis, processing, and alarming, which helps detect and handle abnormal cases swiftly. It saves time wasted on manual analysis, optimizes human resources distribution, and enhances working efficiency.
1. Customers’ Demands: to make comprehensive plans for customers to manage distribution losses and process, and to help introduce technologies and system platforms.
2. Distribution Losses Information Collection List: filled in by water supply enterprises.
3. Pilot Area Division: to set pilot areas, assure that every single household in these areas are not omitted and to implement plans to control distribution losses.
4. Boundary Cleaning: to clarify the pipeline network and the direction of water flows in pilot areas and add flow meters or valves if necessary.
5. Nighttime Water Flow Observation: to analyze changes of water flows at night and to calculate the distribution losses in pilot areas.
6. General Investigation on Water Meters and Usage Violations: all of the large-diameter water meters must receive general investigation. Residential water meters are selectively evaluated. We will consider extending the scope of general investigation if problems of stealing water such as private connections to water pipelines and dismantle of water meters are frequently found.
7. Step-by-step Closed Water Test: to find out the severely afflicted area of leakage.
8. Leak-Checking: to check leakages through techniques such as nighttime flow observation, step-by-step sealed water test, and acoustic leakage-detection and to fix leakage problems of pipeline.
9. Water Meter Replacement: to replace bad, old, and inaccurate water meters detected in the process of general investigation and leakage-checking.
10. Calculation of the Gross Distribution Loss: to analyze the water flowing in and out of the region, the nighttime flow and to make a contrast with the data before partition so as to form a final report.